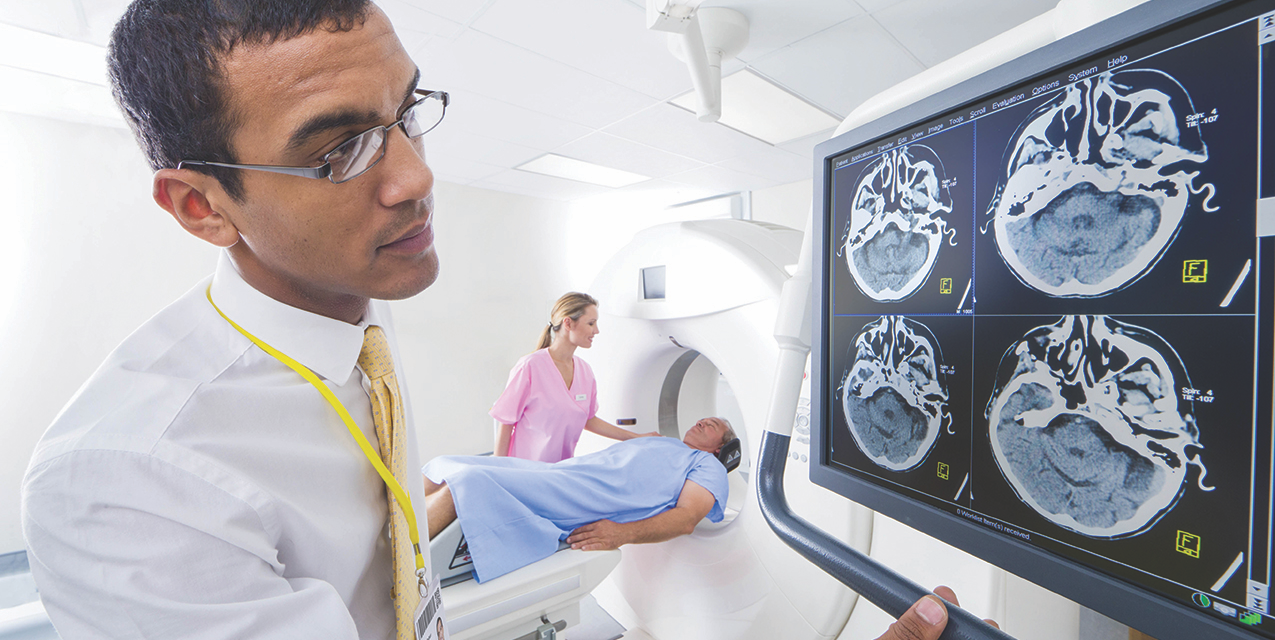
Brain injuries are nothing to take lightly. According to the spinal cord and brain health services provider Newsome Melton, 1.4 million people experience traumatic brain injuries in the United States each year. Brain injuries, which can be traumatic brain injuries (TBI), or acquired brain injuries (ABI), can result from a variety of activities, accidents, and other risk factors. A greater understanding of potential red flags for brain injuries can help people protect themselves against these potentially debilitating and even deadly outcomes.
What’s the difference between TBI and ABI?
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is generally caused by a blow or some other trauma to the head. The injury does not always include an open head wound or skull fracture, nor does loss of consciousness have to occur for an injury to be considered a TBI.
An acquired brain injury (ABI), also called a non-traumatic brain injury, generally results from an illness or condition within the body. The most common causes of ABIs are due to stroke, caused by poor blood flow to the brain from a blockage or bleeding; hypoxia, which is a lack of oxygen; tumors; cancer; or infections that lead to inflammation.
The leading causes of traumatic brain injuries, based on data compiled by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, are:
- Falls: Slipping and falling and hitting the head account for 28% of TBIs. Children between the ages of zero and four, and adults ages 75 and older, are most at risk.
- Motor vehicle accidents: A car or motorcycle crash produces the highest number of TBIs that require hospitalization. In this category, teens between the ages of 15 and 19 account for the most incidents.
- Sports: Roughly 19% of traumatic brain injuries occur when the head is struck forcefully by another object, or against one. Sometimes called mild traumatic brain injuries, some are treated without hospitalization. Recreation- and sports-related injuries tend to fall into this category.
- Assaults: Victims of assault, when one is hit in the head by fists, another object, or even kicked, can cause a TBI. Some TBIs also are caused by firearms.
- Military activity: People in the military can suffer brain injuries from flying debris and large blasts.
- Shaken baby syndrome: This condition occurs when babies are shaken with such force that their brains move violently in the undeveloped skull, causing trauma and damage to brain tissue.
Symptoms of a brain injury can include confusion, trouble communicating or speaking, memory impairments, difficulty with focus and logic, headache, balance issues, vision problems, seizures, trouble swallowing, or personality changes.
Brain injuries can sometimes be prevented with care. A doctor should be contacted immediately when anyone experiences a brain trauma.