Courtesy NIH.gov
Rate of Infection. Infections are increasing in the U.S., with 38,010 new cases daily mostly due to the Omicron BA.2 variant.
COVID Vaccines. 77.3% of the U.S. population received one vaccine, and 65.8% received two. 49.6% of those eligible have not received a booster. Individuals boosted are 21-times less likely to die from COVID and 7-times less likely to be hospitalized. All eligible adults, adolescents, and children 5 and older should be vaccinated and boosted.
Treatment. Mild COVID symptoms can be treated with over-the-counter medicines, such as acetaminophen. If you have COVID and are at risk for severe COVID illness, ask your doctor about monoclonal antibodies (available at infusion centers). Monoclonal antibodies help the immune system recognize and defend against COVID.
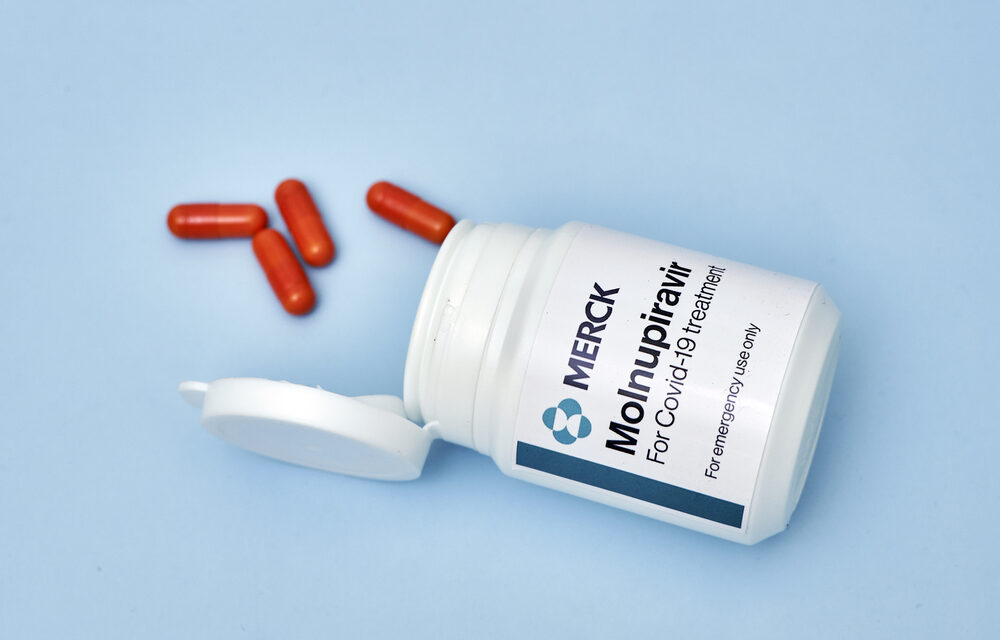
New COVID Pills. A treatment combination of two tablets called Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) can be taken together twice daily for five days. Alternatively, another pill called Molnupiravir, is also taken twice daily for five days. Either option should be taken as soon as possible after symptoms begin. Call your doctor for a prescription.
When to Go to the Hospital. People with serious COVID illness should go to the hospital for treatments. These include antivirals such as remdesivir, which helps slow the virus’s spread. Other available treatments include blood thinners to prevent blood clots, and those that help calm the body’s immune system to prevent worsening disease, resulting in possible tissue and organ damage.
Preventing COVID. Preventing COVID is more effective than treating it. Vaccines help protect people from getting COVID and becoming severely ill. Masks and social distancing help keep the virus from spreading. Getting vaccinated protects everyone and prevents variants. Schedule yours at See https://www.vaccines.gov.